Ear Pain or Clogged Ears with A Sinus Infection | Medyblog

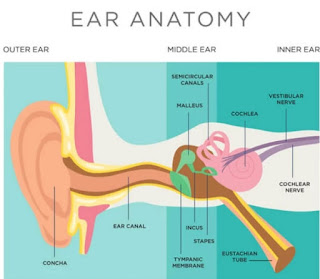
Middle Ear Infections or Otitis Media are secondary infections or side effects of other infections like rhinitis ( common cold ) or chronic sinusitis ( inactive sinus infection). Clogged or Blocked Ears and ear pain indicate a middle ear infection . Fever and ear discharge could be other Symptoms of Middle Ear Infection . Why does chronic sinusitis cause ear pain or clogged ears? In acute sinusitis or active sinusitis, the excess fluid secreted in sinuses is flushed out through the nose. In contrast to acute sinusitis, mucus travels from the sinuses to the throat in chronic sinusitis. In chronic sinusitis or low-grade sinusitis, the infection has lived in the body for such a long time that the body and sinus infection find a balance to coexist peacefully. Our body uses around 200 ml of water which contains proteins, to clean our nose and sinuses and clear dust, bacteria, viruses, and fungi that enter when we breathe external air. With a runny nose, we lose water and...